AI placement in your app matters. It impacts speed, security, cost, and user experience. Here’s the key takeaway:
- Frontend AI runs on the user’s device. It’s great for real-time features like instant text suggestions or gesture tracking. It reduces latency and keeps data private but depends on user hardware and works best with small models (<10MB).
- Backend AI operates on servers. It’s ideal for heavy tasks like data processing, predictive analytics, and large-scale workflows. It offers more power and security but comes with network delays and higher costs.
Quick Overview:
- Frontend AI: Faster responses, lower server costs, privacy-focused, hardware-limited.
- Backend AI: Handles complex tasks, scales easily, requires strong infrastructure, higher latency.
Choosing the right placement depends on your app’s needs. Want speed and privacy? Go frontend. Need power and scalability? Backend is the way. For the best results, combine both strategically.
Full Architecture of a Real AI Mobile App (Backend, Frontend, Infra)
sbb-itb-51b9a02
Frontend vs Backend: Core Differences and AI’s Role
The frontend is like the dashboard of a car – what users see and interact with – while the backend is the engine running everything behind the scenes [11]. This distinction plays a crucial role in determining where AI fits into your system architecture. Let’s break down how these differences shape AI’s placement and functionality.
Frontend AI operates directly in the browser, using tools like TensorFlow.js or WebGPU. Its primary focus is enhancing the user experience with features like real-time gesture tracking, instant text suggestions, or interfaces that adapt in real-time without waiting for server responses. The catch? It’s limited by the hardware of the user’s device, so model sizes need to stay small. For example, BudouX, a model for text breaking, is just 9.4KB – a perfect fit for frontend deployment [5].
Backend AI, on the other hand, works on servers and handles the heavy lifting. It manages tasks like complex data processing, large-scale embeddings, and workflows like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) that pull from vast vector databases.
"Front-end AI refers to AI technology used up-front, often as the face of a product or service… In contrast, Back-end AI refers to AI technology used behind the scenes."
- Donggyu Kim from USC’s Annenberg School [9]
Client-side AI excels in delivering low latency and maintaining user privacy but is constrained by the user’s hardware. Server-side AI offers powerful computation and security but may introduce network delays. A practical guideline for frontend AI is to keep model sizes under 5MB, aligning with the 75th percentile of web page sizes [5].
Frontend: User-Facing Interfaces and User Experience
When it comes to the frontend, AI is all about improving how users interact with a product. The frontend includes everything users directly engage with – buttons, forms, navigation menus, and visual layouts. Built using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, it’s the graphical user interface (GUI) that determines whether a product feels intuitive or clunky [3][11].
AI transforms these static interfaces into dynamic, responsive environments. Running directly in the browser, client-side AI provides near-instant feedback and personalized experiences [5]. This enables features like real-time language translation, gesture-based controls, and layouts that adapt to user behavior on the fly.
However, frontend AI relies on lightweight, task-specific models rather than large-scale ones. For instance, MediaPipe’s language detection model is just 315KB, making it ideal for browser-based use [5].
Backend: Server-Side Logic and Data Management
The backend is the powerhouse of any application – handling data processing, managing databases, and executing core business logic [3][11]. While users don’t interact with it directly, the backend ensures every feature on the frontend runs smoothly.
Backend AI is built for scale, capable of processing thousands of requests simultaneously, generating embeddings from massive datasets, running predictive analytics, and managing complex workflows. Whether it’s searching through millions of documents using vector similarity or training models on proprietary data, the backend is where this heavy lifting happens [8][12].
Security and performance are key considerations here. Backend AI safeguards sensitive algorithms, API keys, and proprietary models, keeping them hidden from public access. This level of protection is crucial for preventing API abuse and protecting intellectual property.
"While most AI features on the web rely on servers, client-side AI runs directly in the user’s browser."
- Maud Nalpas from web.dev [5]
That said, client-side AI comes with tradeoffs. When code runs in the browser, it’s exposed to potential inspection, making it harder to protect sensitive components. By contrast, backend AI provides the necessary isolation and control to keep these elements secure.
AI in Frontend Development: Improving User Experiences
AI is reshaping frontend development by enabling instant, on-device processing, which results in highly responsive and personalized user experiences. By processing data directly on the user’s device, AI eliminates the delays caused by server interactions. This shift has brought a new focus on creating context-aware interactions [16].
The choice of implementation depends on your specific needs. For example, tools like TensorFlow.js enable on-device machine learning, which offers benefits like enhanced privacy and reduced latency. On the other hand, cloud APIs are better suited for tasks that require heavy computational power [16]. As of March 2025, 78% of organizations have adopted AI for at least one business function, with 63% using it for tasks like text generation [16].
"The question isn’t if your applications will incorporate AI, but how and when."
- Deepa Subramanian, Tech Enthusiast [16]
Although 82% of frontend developers have experimented with AI tools, only 36% have integrated these tools into their daily workflows as of 2025 [13]. A practical starting point? Prototype a single feature, such as smart search or content summarization, and gauge user engagement before scaling up [15][10].
Personalized User Interfaces
AI has revolutionized user interfaces by tailoring them to individual behaviors rather than presenting a one-size-fits-all layout. Vector-based personalization dives deeper into user context, moving beyond simple keyword matching. For instance, if someone explores "Modern JavaScript Frameworks", the system might suggest "React" or "Next.js", even if those specific terms weren’t searched [15].
Semantic search takes personalization a step further by understanding user intent. A query like "comfy sneakers for long walks" could return results for "memory-foam sneakers", even if the product description doesn’t include the exact words. This is powered by vector embeddings, which identify conceptually similar items instead of just matching text [15].
Generative UI, meanwhile, dynamically adjusts layouts, themes, and navigation based on predictions of user behavior. Unlike static pages, these adaptive interfaces evolve as users interact with them. By 2028, over 20% of workplace applications are expected to use AI-driven personalization algorithms [16].
| AI Component | Frontend Role | Implementation Example |
|---|---|---|
| Chatbots | Conversational UI & Support | Next.js + OpenAI API [15] |
| Semantic Search | Intent-based Discovery | Vercel AI SDK + Pinecone [15] |
| Summarization | Content Accessibility | Chrome Summarizer API [16] |
| Recommendations | Contextual Personalization | Vector Embeddings [15] |
| Generative UI | Dynamic Layout Adjustment | Real-time behavior analytics [10] |
To make these personalized interfaces efficient, deploy AI API calls closer to users using edge functions to reduce latency [15]. Cache responses with tools like Redis or Next.js Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR) to cut down on API costs [15]. Additionally, the Compute Pressure API can assess whether a user’s device can handle large client-side AI tasks before initiating downloads [5].
AI-powered personalization doesn’t stop at displays – it continues to enhance user journeys with real-time adjustments.
Adaptive UX and Real-Time Interactions
AI takes user experience to the next level by adapting interfaces in real time based on user behavior. Unlike static designs that rely on manual coding for every detail, AI uses pattern recognition to automate layout changes and optimize media [2].
The difference is clear in how interfaces respond. Traditional designs offer standardized experiences for all users, while AI tailors interactions based on individual behaviors [2][10]. For example, AI can analyze user actions as they happen, adjusting UI elements, navigation, and content recommendations dynamically – no page refreshes or server delays required.
Predictive UX is another game-changer. It simulates interactions to identify potential friction points before they occur, offering a proactive approach compared to traditional reactive testing [2]. AI tools can also optimize image and video quality automatically based on the user’s device and internet connection, ensuring faster load times without manual intervention [2].
| Feature | Traditional Static Design | AI-Driven Adaptive UX |
|---|---|---|
| Layout | Fixed/Responsive (Manual) | Dynamic/Generative (Automated) [2] |
| User Interaction | Standardized for all users | Personalized based on behavior [2][10] |
| Development | Manual coding, time-heavy | Rapid prototyping, AI-assisted [13] |
| Maintenance | Manual updates | Pattern-based learning [2] |
| Testing | Reactive (user feedback) | Predictive (simulated interactions) [2] |
Voice and gesture interfaces are also gaining traction, moving beyond traditional clicks and taps. With Natural Language Processing (NLP) and computer vision, touchless and emotionally responsive interactions are becoming a reality [2]. To maintain smooth performance, resource-heavy tasks can be offloaded to Web Workers, keeping the main thread free and the interface responsive [5].
For startups with limited resources, AI can be a game-changer, automating routine tasks like coding, testing, and documentation. A good strategy? Focus on writing 80% of the core logic manually while letting AI handle the repetitive 20% [13][18].
As adaptive interfaces evolve, conversational AI is stepping into the spotlight with context-aware assistance.
Chatbots and Intelligent Assistants
Conversational AI has grown from basic chatbots into agentic systems capable of completing tasks independently [17]. For seamless implementation, it’s crucial to use effective communication methods. WebSockets or Server-Sent Events (SSE) allow for streamed responses, letting users see "typing" effects or interact with partial results, which makes conversations feel more natural [14].
UI-consumable contracts ensure that response schemas are standardized. By defining types like ‘text,’ ‘code,’ or ‘tool_call,’ the frontend can render interactive components – such as maps or graphs – instead of just plain text [14]. For example, an AI agent could return a WeatherCard or an InlineEditor that the frontend interprets as a functional component [14].
Local memory management can also reduce server load. State management tools like Pinia, Zustand, or Redux allow agents to maintain context locally, avoiding the need to send full conversation histories back to the server with every interaction [14].
Two key orchestration patterns are commonly used: the Manager Pattern, where a central agent coordinates specialized agents via tool calls, and the Decentralized Pattern, where peer agents hand off tasks based on their expertise [17].
While smaller models like BudouX (9.4KB) and MediaPipe’s language detection (315KB) are lightweight, larger generative models like Gemma 2B can reach sizes of 1.3GB – over 100 times the size of the average web page [5]. To manage this, use the Cache API to store models locally and provide progress indicators for large downloads to set user expectations [5].
Reliability is key. Implement guardrails like relevance classifiers and PII filters to flag off-topic queries and protect sensitive data [17]. For high-risk tasks, such as processing refunds, ensure the AI escalates to a human representative rather than acting autonomously [17].
"Integrating AI agents isn’t just about wiring up an API. It’s about making unpredictable, evolving behavior feel natural and reliable in your app."
- Tom Yahav, Full Stack Engineer [14]
AI in Backend Development: Automation and Intelligence
While frontend AI focuses on delivering immediate, tailored experiences, backend AI handles the heavy lifting behind the scenes. It processes massive datasets, coordinates complex workflows, and makes critical decisions to ensure your product runs efficiently. Acting as the orchestration layer, backend AI manages conversation states, tool execution, and long-term memory across various channels, forming the backbone of autonomous systems [19][7]. In essence, it supports and elevates your product’s overall functionality.
Unlike traditional rule-based systems that rely on fixed checklists, AI agents excel at handling ambiguous, context-rich tasks like fraud detection or vendor security reviews. They can identify subtle patterns that static systems often miss [17].
Adoption of these technologies is accelerating. Gartner projects that by 2026, 40% of enterprise applications will include task-specific AI agents, a significant leap from under 5% in 2025 [19]. This isn’t just about faster operations – it’s about creating systems that can plan, execute, and adapt with minimal human input.
"In 2026, conversational AI is best understood as a network of tools, policies, memory, and real-time state – not a single prompt."
Backend AI also optimizes processes by using model routing. Simple tasks, like text classification, are assigned to smaller, faster models, while more resource-intensive reasoning models handle complex problems. This approach balances performance and cost, ensuring you’re not overpaying for computational resources when a simpler model is sufficient [7][20].
Data Processing and Predictive Analytics
Backend AI turns raw data into meaningful insights by cleaning, segmenting, and generating vector embeddings that feed into Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines [22]. This goes beyond basic number crunching – it identifies patterns that would be impossible to spot manually.
Deterministic data processing bridges AI reasoning with precise calculations. Tools like "Code Interpreter" enable AI to write and execute Python scripts for mathematical analysis, providing exact results rather than estimates [20]. For example, instead of guessing financial projections, the AI can calculate precise figures based on your data.
Stateful memory systems enhance this capability by storing session data and long-term memory banks. This allows the AI to build on past interactions, offering more personalized and relevant insights over time [7]. Instead of starting fresh with each request, it learns and adapts, improving its responses.
For scalable systems, external state management is crucial. Services like Redis or Firestore store session data, enabling horizontal scaling to handle thousands of simultaneous requests without performance bottlenecks [7]. This ensures your AI backend keeps pace as your user base grows.
Once data insights are refined, backend AI seamlessly automates entire workflows.
Workflow Automation and Decision-Making
Backend AI shines in automating complex workflows that traditionally required human oversight. By integrating with external APIs – like CRMs, databases, and payment systems – AI agents can autonomously perform tasks such as filing tickets, updating records, scheduling calls, and even processing refunds [19][17].
A key feature is the "tool registry" model. Here, the language model selects the appropriate tool for a task, but the backend enforces permissions based on business rules and user roles [19]. This ensures flexibility in decision-making while preventing unauthorized actions.
Agentic tasks often involve multiple steps and can take several minutes, breaking away from the typical "single request/response" API pattern [19]. To handle this, asynchronous methods like WebSockets or server-side events are preferable to avoid timeouts, which can occur after 29 seconds [21].
Using a "manager" pattern helps coordinate specialized sub-agents. Instead of burdening a single agent with multiple responsibilities, tasks are divided among agents with specific expertise – one might focus on research, another on writing, and a third on triage [17]. This approach prevents inefficiencies and overload.
For high-stakes actions, human-in-the-loop triggers are essential. Establish clear thresholds for when AI should escalate tasks, such as large refunds or critical system changes, to a human operator [17]. This ensures that while automation increases efficiency, it doesn’t compromise safety or introduce unacceptable risks.
Security and Threat Detection
Backend AI plays a vital role in bolstering security and detecting threats, making systems more resilient. It continuously monitors activity in real time, identifying suspicious behavior and contextual anomalies that traditional rule-based systems might overlook. Instead of following a checklist, AI acts as an investigator, uncovering issues even when explicit rules aren’t violated [17].
Implement multi-layered guardrails to maintain data integrity. These include relevance classifiers to filter off-topic queries, PII filters to prevent sensitive data leaks, and safety classifiers to block harmful outputs [17][20]. Together, these measures ensure that AI interactions remain within safe and acceptable boundaries.
AI Gateways centralize security controls by managing API keys, enforcing authentication protocols like OAuth, and monitoring for potential vulnerabilities such as prompt injections or data breaches [22][17]. This unified approach simplifies governance while enhancing visibility into how AI systems interact with your infrastructure.
For models requiring up-to-date information, backend tools like web search enable access to current data without compromising security. For example, OpenAI’s GPT-5, with a training data cutoff in late September 2024, can rely on such tools to stay informed [20]. By carefully controlling which external sources the AI can access, you maintain data integrity while enabling real-time intelligence.
To maintain stability, version-control prompts alongside your application code. This ensures validated configurations are deployed across development, staging, and production environments, reducing the risk of unexpected behavior in live systems [22].
Key Differences: When AI Belongs in the Frontend vs the Backend
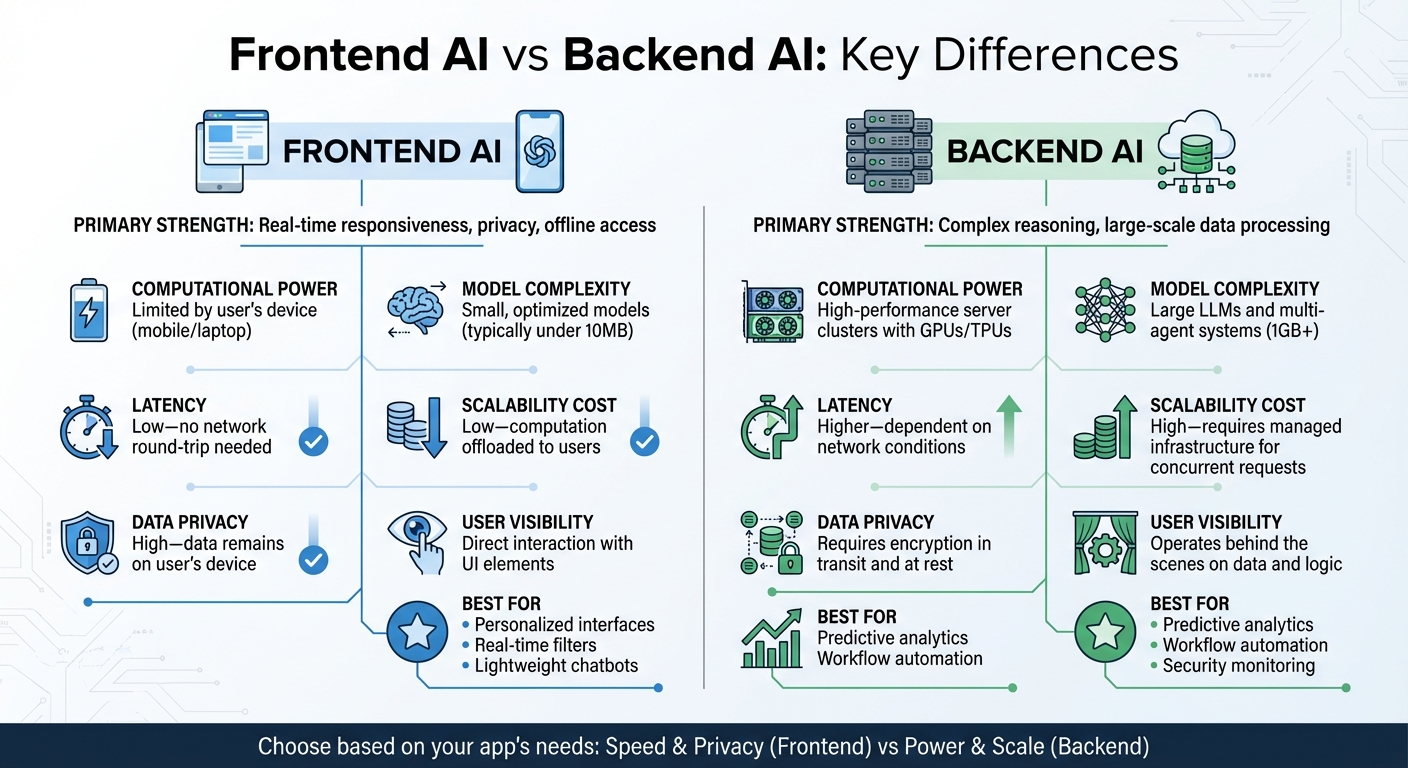
Frontend vs Backend AI: Key Differences, Capabilities and Use Cases
Where you position AI – whether in the frontend or backend – can have a major impact on user experience, costs, and scalability. Each approach comes with its own strengths and trade-offs.
Frontend AI operates directly on the user’s device, offering immediate responses, enhanced privacy, and offline functionality. By running locally, it reduces latency and keeps data on the device, making it a great choice for privacy-sensitive applications. However, its performance is tied to the user’s hardware, which can limit its capabilities. On the other hand, Backend AI is designed for heavy lifting. It excels at handling complex reasoning, processing large-scale data, and running resource-intensive tasks using high-performance GPUs or TPUs. But this comes with added network latency and higher infrastructure costs, especially as the user base grows [7].
Data privacy is another key distinction. With Frontend AI, sensitive data never leaves the device, making it ideal for applications where privacy is critical [23]. Backend AI, however, requires data to travel to and from servers, demanding robust encryption and strict access controls.
"Frontends are no longer written only for humans. AI tools now actively work inside our codebases."
Frontend AI typically relies on smaller, optimized models, while backend systems support much larger models capable of more sophisticated tasks. The table below provides a clear breakdown of how these two approaches compare in terms of capabilities, constraints, and ideal use cases.
Comparison Table: Capabilities, Constraints, and Use Cases
| Dimension | Frontend AI | Backend AI |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | Real-time responsiveness, privacy, offline access [23] | Complex reasoning, large-scale data processing [7] |
| Computational Power | Limited by the user’s device (mobile/laptop) [23] | High-performance server clusters with GPUs/TPUs [7] |
| Model Complexity | Small, optimized models (typically under 10MB) [5] | Large LLMs and multi-agent systems (1GB+) [7] |
| Latency | Low – no network round-trip needed [5] | Higher – dependent on network conditions [23] |
| Scalability Cost | Low – computation is offloaded to users [23] | High – requires managed infrastructure for concurrent requests [7] |
| Data Privacy | High – data remains on the user’s device [23] | Requires encryption in transit and at rest [3] |
| User Visibility | Direct interaction with UI elements [3] | Operates behind the scenes on data and logic [3] |
| Best For | Personalized interfaces, real-time filters, lightweight chatbots | Predictive analytics, workflow automation, security monitoring |
Understanding these differences helps you choose the right approach based on your application’s needs and the experience you want to deliver to users.
Decision Framework: Choosing the Right Placement for AI in Your Startup
When deciding where to integrate AI into your startup, it’s crucial to align its placement with both your technical capabilities and business objectives. As mentioned earlier, frontend AI and backend AI serve different purposes. Frontend AI is ideal for tasks like real-time personalization or instant user interactions, where avoiding server delays is critical. On the other hand, backend AI is better suited for handling large datasets, running predictive analytics, or managing complex business logic behind the scenes [24][25].
Your current infrastructure maturity plays a big role in this decision. If your startup already has a robust web application infrastructure with secure authentication, frontend AI can be seamlessly deployed. However, if you’re building a platform that caters to multiple clients – such as mobile apps, web interfaces, or APIs – a Standalone Toolkit approach with backend AI may be more effective. This setup offers centralized control and ensures consistency across various endpoints [6].
Another key consideration is your team’s skill set. Frontend-focused teams need to excel in AI prompting and code review to ensure a smooth user experience. In contrast, backend teams must be proficient in areas like ML Ops, system architecture, and AI orchestration.
"The future isn’t about AI replacing developers, but about developers evolving into roles where they collaborate with, oversee, and augment AI systems."
- Inga Raziya, Columbia Business School [25]
If your team lacks expertise in backend AI, it’s important to plan for additional development time. Backend AI typically requires about 25% more time to implement compared to frontend solutions [26].
Cost and scalability are also critical factors. Client-side AI shifts computation to users’ devices, which can reduce server costs and make free service tiers more sustainable [23]. In contrast, backend AI relies on managed infrastructure that must scale with increased demand, leading to higher costs as your user base grows [7]. To guide your decision-making, frameworks like the VIA-AI Framework can help assess factors such as value potential, integration feasibility, alignment with goals, data quality, scalability, and security [10].
Lastly, practical deployment considerations should not be overlooked. For frontend AI, ensure you have graceful fallbacks in place, as device capabilities can vary widely. Models ranging from 5MB to 1.5GB may put a strain on mobile data plans [5][23]. For backend AI, incorporating human oversight is essential, especially for tasks like security audits or content moderation. While AI can identify up to 90% of common vulnerabilities, human judgment is still needed for edge cases that require nuanced decisions [25].
Combining Frontend and Backend AI: Building an Integrated Architecture
The most effective AI systems seamlessly combine frontend and backend components to deliver a cohesive user experience. In these architectures, the backend acts as the central hub, handling tasks like managing conversation states, executing tools, and retrieving memory. Meanwhile, the frontend focuses on capturing user input and presenting real-time updates to the user interface [19].
To ensure smooth communication between these layers, standardized protocols play a critical role. For instance, the Model Context Protocol (MCP) standardizes how AI agents access tools and data, functioning much like a "universal port" for AI peripherals [7]. Similarly, the Agent-User Interaction (AG-UI) protocol allows backend agents to trigger frontend updates without creating a tightly coupled system [7][27]. These protocols separate the reasoning logic from specific tool implementations, making the architecture easier to maintain and adapt over time.
For delivering real-time updates, it’s better to move away from traditional polling methods and adopt event-driven approaches like Server-Side Events (SSE) or real-time database subscriptions [19]. For example, when an AI agent completes a multi-step task – such as analyzing data and preparing a report – these event-driven patterns push updates to the frontend immediately. This ensures a smooth and responsive user experience across platforms, whether on web, mobile, or other channels. To further enhance scalability and maintain context across devices, session states can be stored in external systems like Redis or Firestore [7]. These strategies build on earlier concepts, creating a tightly integrated AI system that bridges frontend and backend effectively.
As Nelson Michael aptly points out, "technical debt from neglected architecture becomes a liability" [1].
Security considerations also shape how these integrations are structured. Frontend-first architectures, such as Integrated Copilots, leverage the user’s existing browser session, which simplifies implementation and eliminates the need for complex user impersonation mechanisms often required in backend-first setups [6]. However, for headless AI services catering to multiple clients, a backend-first architecture with a deterministic tool registry is often more suitable. In this model, the backend enforces strict control over which tools the AI can access, ensuring both functionality and security [19].
Conclusion: Aligning AI Implementation with Product Goals
Deciding where and how to implement AI in your product isn’t just a technical choice – it’s a strategic move that should directly align with your business goals. Whether your focus is improving customer experience, cutting operational costs, or speeding up time-to-market, AI should serve as a tool to strengthen those objectives.
This sentiment is echoed by industry leaders:
"AI doesn’t reduce the need for good architecture. It raises the stakes."
- Nelson Michael of LogRocket [1]
The most effective AI strategies are built on solid foundations. Predictable code structures and clear documentation – understandable to both human developers and AI systems – are essential. They help prevent the accumulation of technical debt, which can derail long-term success.
Although 82% of frontend developers have experimented with AI tools, only 36% have managed to integrate them into their daily workflows. This highlights the importance of deliberate, structured integration over casual experimentation [13]. On the other hand, engineering teams that adopt specialized AI tools report productivity gains of 40–42% [4].
To ensure success, a structured framework is key. Tools like VIA-AI can guide you in evaluating potential AI features based on factors such as value potential, ease of integration, alignment with strategy, data quality, and security [10]. Starting small – such as with frontend prototypes – can help prove the value of AI. Once validated, scaling to backend systems becomes more feasible, especially for products requiring advanced reasoning, long-term memory, or enterprise-level security.
"In today’s AI landscape, where language models have become commoditized, the true differentiator lies in frontend development and user experience."
At the heart of successful AI implementation is sound architecture. It’s the foundation that allows startups to scale AI safely and effectively, turning it into a force multiplier that aligns seamlessly with their product goals.
FAQs
How do I decide whether to use AI in the frontend or backend of my application?
Choosing between frontend AI and backend AI boils down to your application’s specific goals and technical requirements.
Frontend AI works best for features that directly interact with users, such as personalized interfaces, real-time interactions, and tailored user experiences. Since it operates in the user’s browser, it offers perks like improved privacy, offline capabilities, and lower server costs. That said, it can be limited by the browser’s available resources, which might impact performance.
On the other hand, backend AI excels at handling tasks that demand significant data processing, automation, or centralized decision-making. With access to powerful computational resources, it can manage heavy workloads efficiently. However, it may introduce delays due to network latency. Backend AI is also a solid choice for systems requiring advanced security measures or centralized data control.
When deciding where to implement AI, think about factors like data sensitivity, performance needs, and user privacy. Matching your approach to your product’s goals and infrastructure will help deliver a smooth user experience while maintaining technical efficiency.
How does combining AI in the frontend and backend improve user experience and system performance?
Integrating AI into both the frontend and backend creates a dynamic combination that improves both user experience and system performance.
Frontend AI is all about creating personalized and interactive experiences for users. It can adapt user interfaces in real time, suggest relevant content, or even tweak layouts based on how users interact with the platform. This makes the experience smoother, more engaging, and tailored to individual preferences.
Meanwhile, backend AI takes care of the heavy lifting behind the scenes. It processes data, automates repetitive tasks, and uses predictive analytics to make smart decisions. By handling these resource-intensive operations, the backend ensures the system stays efficient and responsive.
When these two layers work in harmony, the result is a seamless and intuitive interface for users, supported by a backend that’s capable of managing complex tasks and scaling as needed. Together, they provide a balanced approach to delivering both responsiveness and reliability.
What privacy considerations should I keep in mind when using AI in the frontend versus the backend?
The way AI handles privacy depends on whether it’s operating on the frontend or backend.
Frontend AI runs directly on a user’s device. This setup can improve privacy since sensitive data doesn’t need to leave the device – it stays local. By avoiding data transmission to external servers, the chance of breaches is reduced. That said, protecting the device itself is critical, as local threats could still compromise the data.
Backend AI, in contrast, operates on servers or in the cloud. This method offers more processing power and scalability but requires data to be sent over networks. This introduces potential risks, such as interception or unauthorized access. To address these vulnerabilities, measures like strong encryption, strict access controls, and adherence to data protection laws are essential.
Simply put, frontend AI keeps data closer to the user, reducing exposure, while backend AI demands robust security to safeguard data during transmission and storage.









Leave a Reply